- Home
-
Products
Industrial & Laboratory series New energy storage series Spill prevention containment&protection Office fire-proof series
-
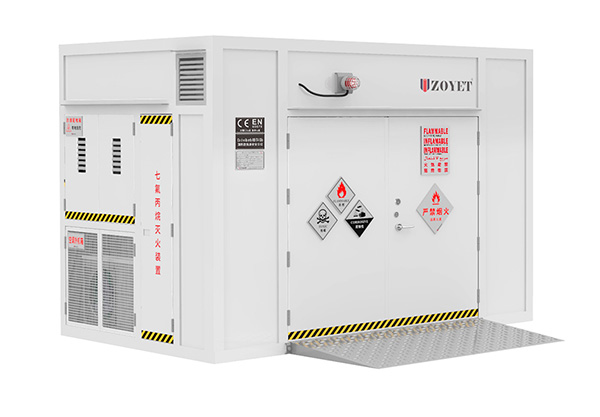 Outdoor chemicals storage container
Outdoor chemicals storage container
-
 Flammable cabinet
Flammable cabinet
-
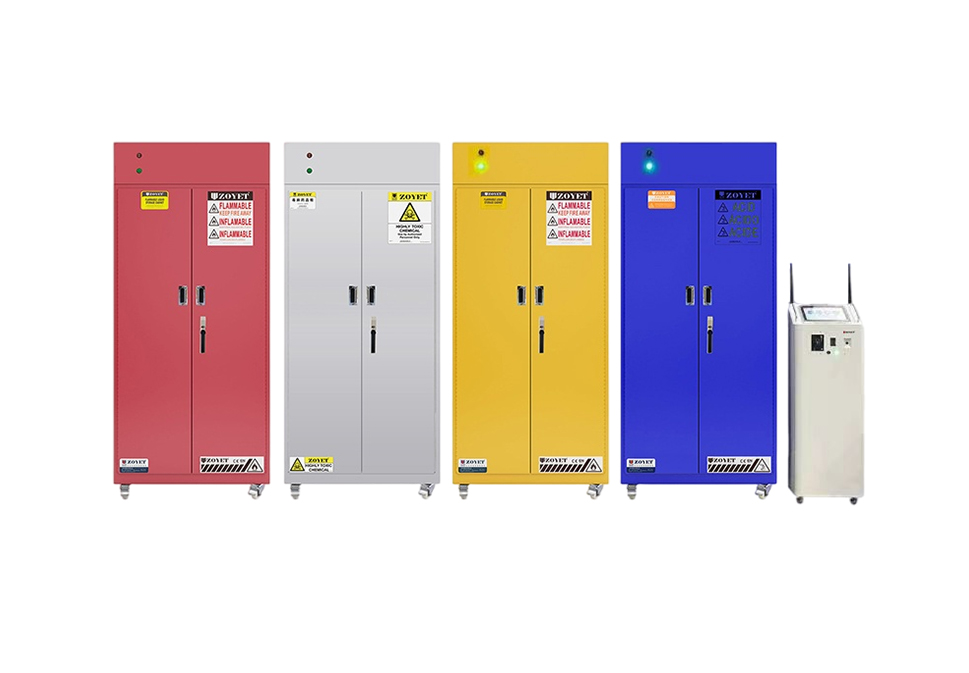 RFID intelligent reagent cabinet
RFID intelligent reagent cabinet
-
 90 minutes safety cabinet
90 minutes safety cabinet
-
 Combustible cabinet
Combustible cabinet
-
 Corrosive cabinet
Corrosive cabinet
-
 Toxic cabinet
Toxic cabinet
-
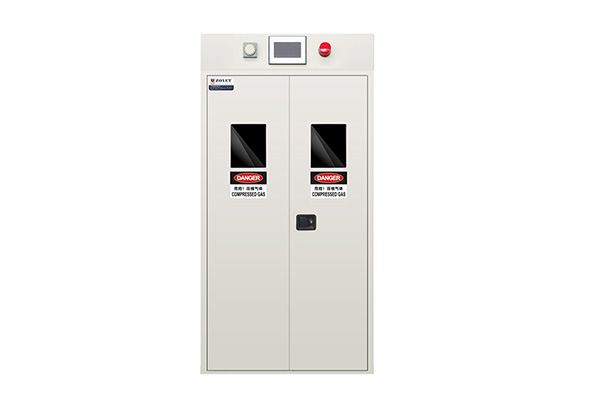 Gas cylinder storage cabinet
Gas cylinder storage cabinet
-
 Gas cylinder storage cage-yellow&green
Gas cylinder storage cage-yellow&green
-
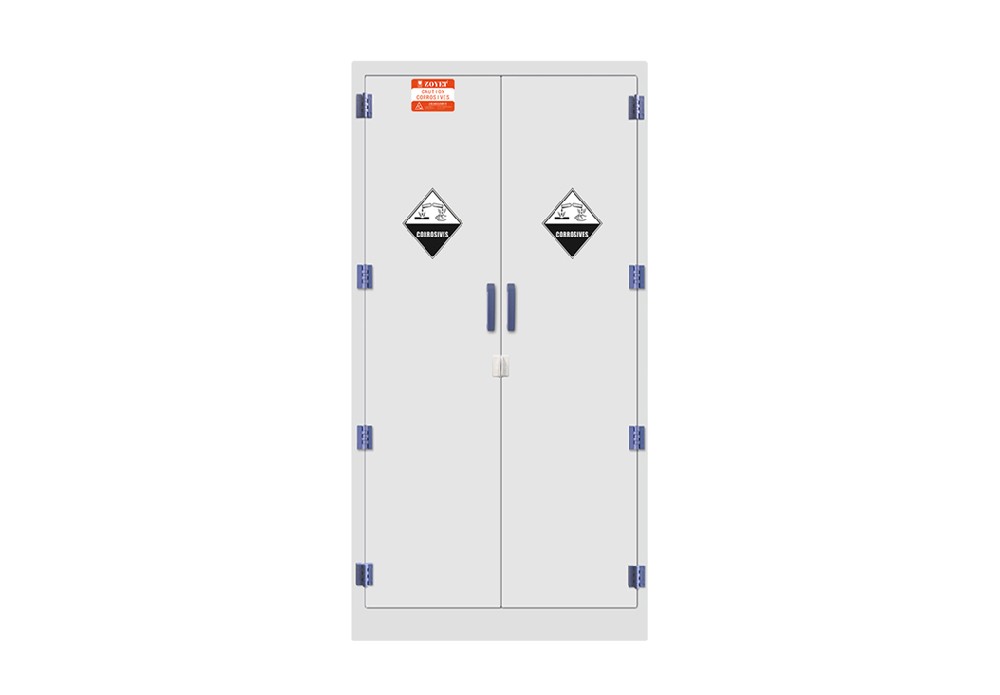 PP Acid cabinet/PP medicines cabinet
PP Acid cabinet/PP medicines cabinet
-
 Fume hood-PP fume hood&Steel fume hood
Fume hood-PP fume hood&Steel fume hood
-
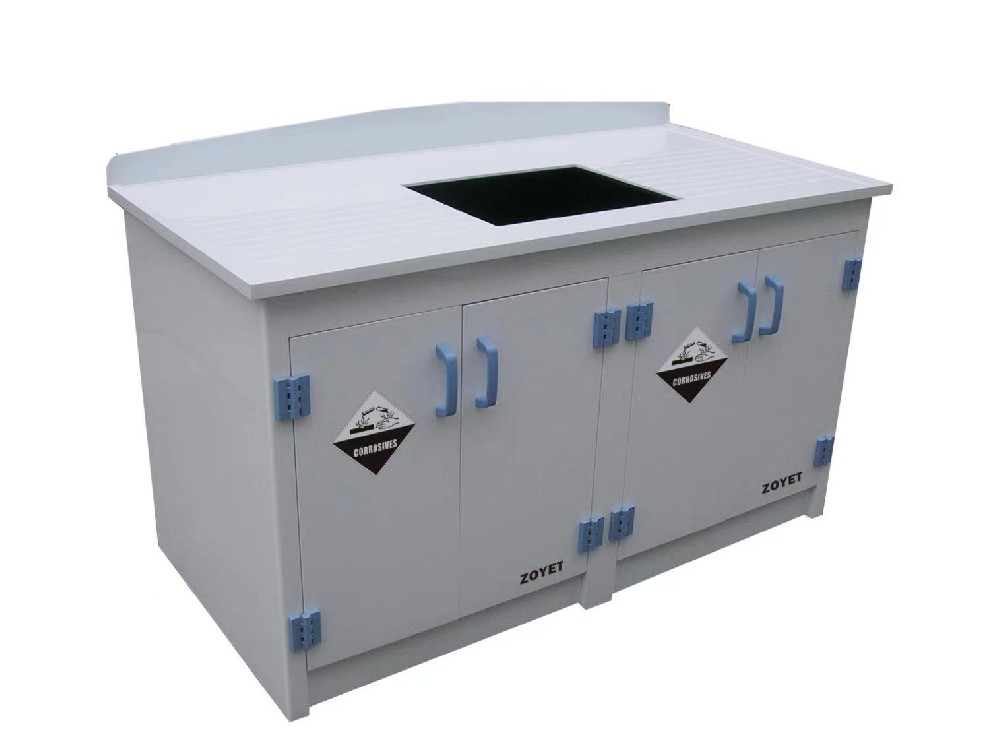 PP Undertable Cabinet
PP Undertable Cabinet
-
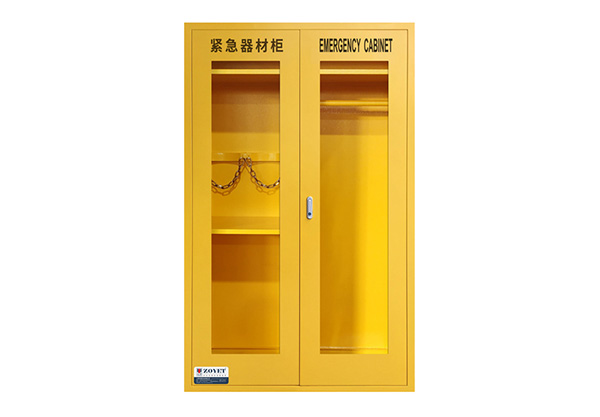 Emergency Equipment & Breathing appratus Cabinet
Emergency Equipment & Breathing appratus Cabinet
-
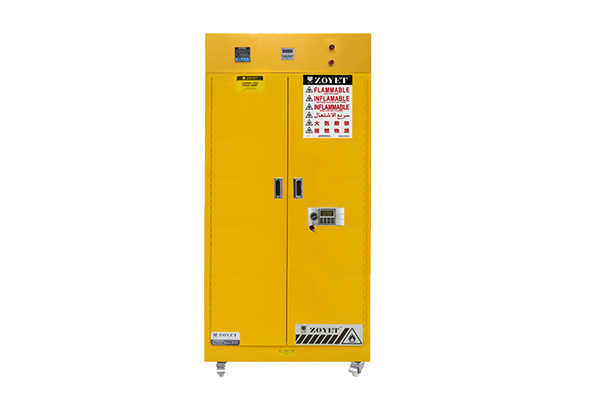 Intelligent safety cabinet
Intelligent safety cabinet
-
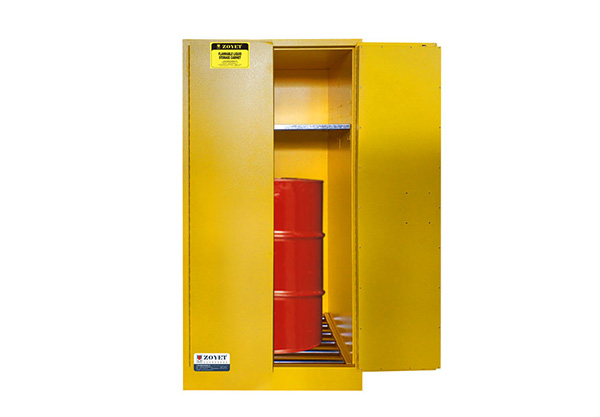 Drum storage cabinet
Drum storage cabinet
-
- Solution
- RFQ
- News
- About Us

What is EPA Certification?
The EPA directs environmental science, research, education, and assessment efforts in the United States.
(1) Regulation development and Enforcement: EPA develops and enforces regulations in accordance with environmental laws enacted by Congress. The EPA is responsible for researching and developing national standards for various environmental programs and delegating responsibility to state governments and Native American tribes for licensing, monitoring, and enforcement. If national standards are not met, EPA can sanction or take other measures to assist state governments and Native American tribes in meeting environmental quality requirements.
(2) Providing financial assistance: In recent days, the EPA has spent 40 to 50 percent of its Congressionally approved budget directly funding state environmental programs by applying for funds. Epa provides funds to state governments, nonprofit agencies, and educational institutions to support high-quality research, enhance the scientific basis for national environmental decision-making, and help achieve EPA's goals.
The EPA provides research funding and graduate scholarships. Epa supports environmental education programs to increase public awareness, knowledge, and skills to make the best decisions affecting environmental quality. Epa also provides information on environmental financing services and programs to state and local governments and small businesses. Epa also provides other financial assistance through a number of programs: the State Drinking Water Revolving Fund, the State Clean Water Revolving Fund, and Brown Land Cleanup and Reuse.
(3) Conducting environmental research: With research laboratories located throughout the country, EPA is committed to assessing the state of the environment in order to identify, understand, and address current and future environmental problems; Integrating the research results of scientific partners, including state institutions, private organizations, academia, and others; Lead the identification of emerging environmental issues and improve the technical level of risk assessment and risk management.
(4) Sponsoring voluntary partners and programs: Through its headquarters and field offices, EPA works with more than 10,000 factories, businesses, nonprofits, and state and local governments on more than 40 voluntary pollution prevention programs and energy conservation efforts. The partners have set voluntary pollution management targets, such as water and energy conservation, greenhouse gas reduction, significant reductions in toxic emissions, solid waste reuse, indoor air pollution control, and pesticide risk control. The EPA returns the favor with incentives, such as a voluntary partner for important public recognition projects and access to up-to-date data.
(5) Strengthening environmental education: The Ministry of Environmental Protection strives to develop education to foster public awareness and responsibility for environmental protection, and to inspire individuals to develop a sense of responsibility for protecting the environment.

 Language
Language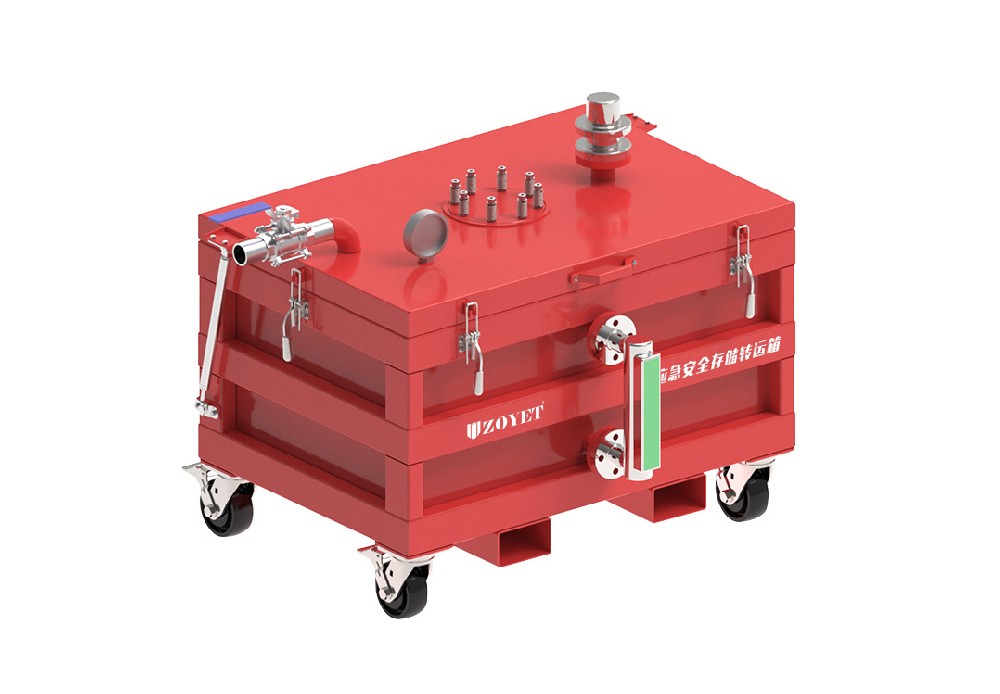 Battery safety storage box
Battery safety storage box
 Battery recharging cabinet
Battery recharging cabinet
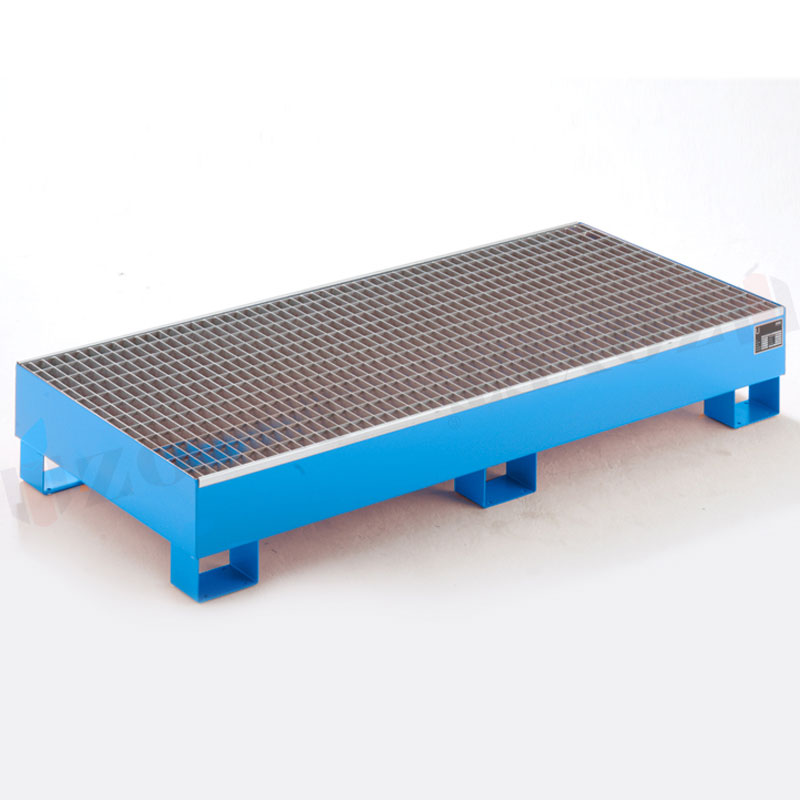 Steel spill pallet
Steel spill pallet
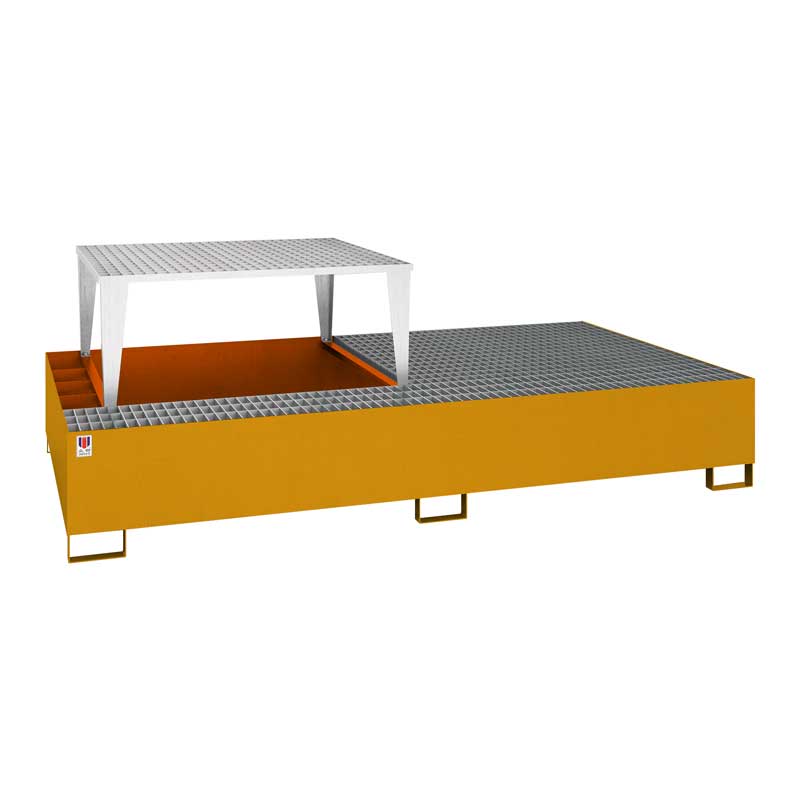 Steel spill pallet for IBC tank
Steel spill pallet for IBC tank
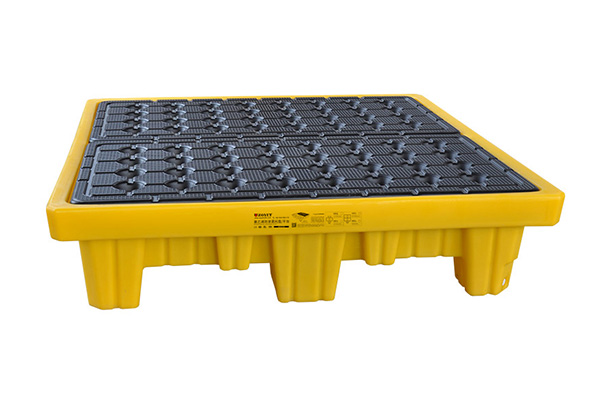 PE spill pallet
PE spill pallet
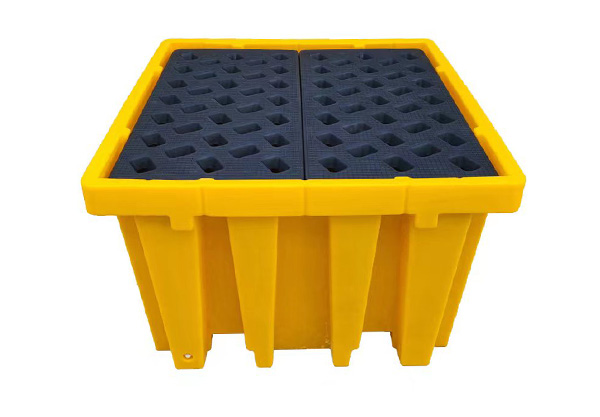 PE IBC spill pallet
PE IBC spill pallet
 Countertop stainless steel tray
Countertop stainless steel tray
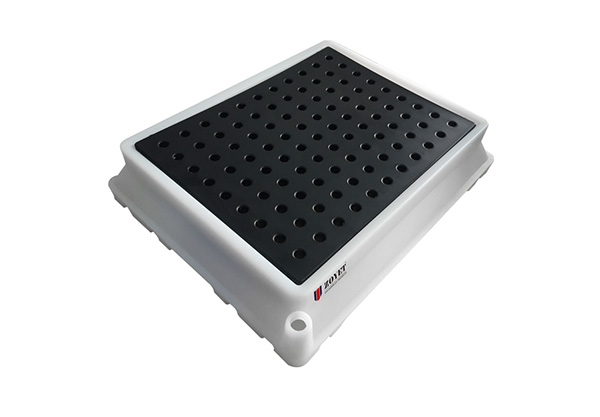 Countertop spill containment tray
Countertop spill containment tray
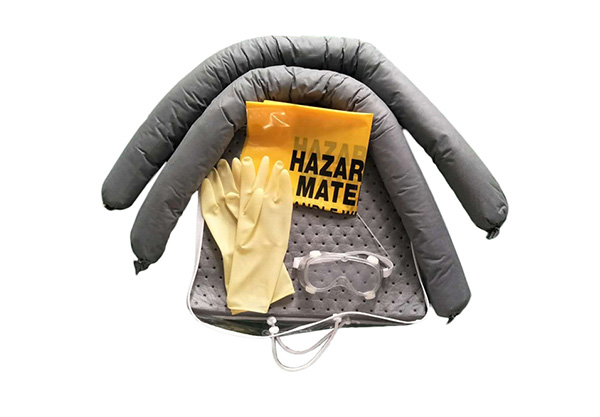 Adsorbent kit
Adsorbent kit
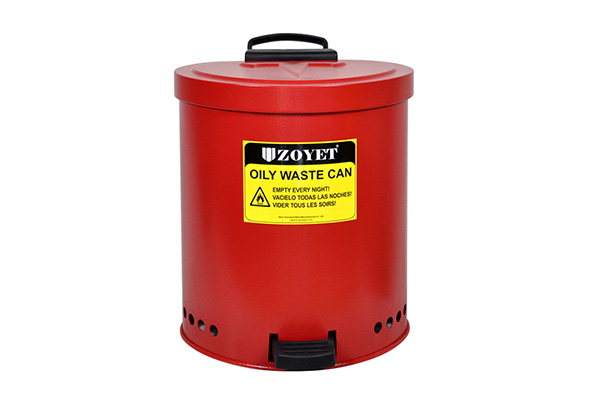 Oily waste can
Oily waste can
 Biochemical trash can
Biochemical trash can
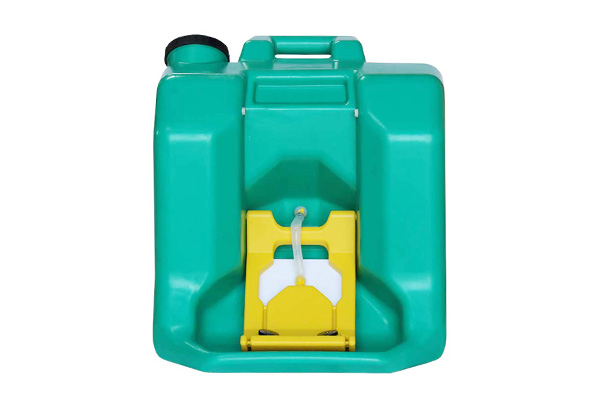 Eye wash
Eye wash
 Fire resistant filing cabinet
Fire resistant filing cabinet
 Fire resistant safes
Fire resistant safes
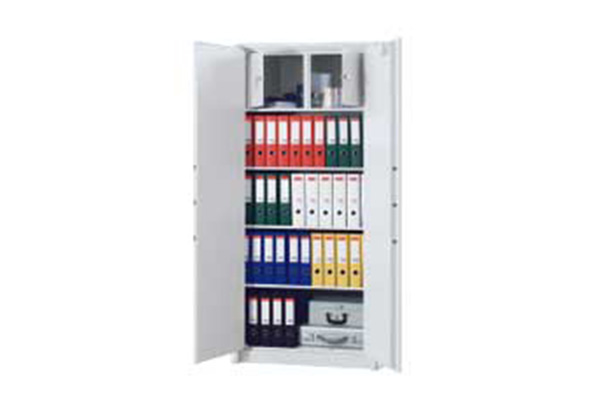 Fireproof filing cabinet
Fireproof filing cabinet